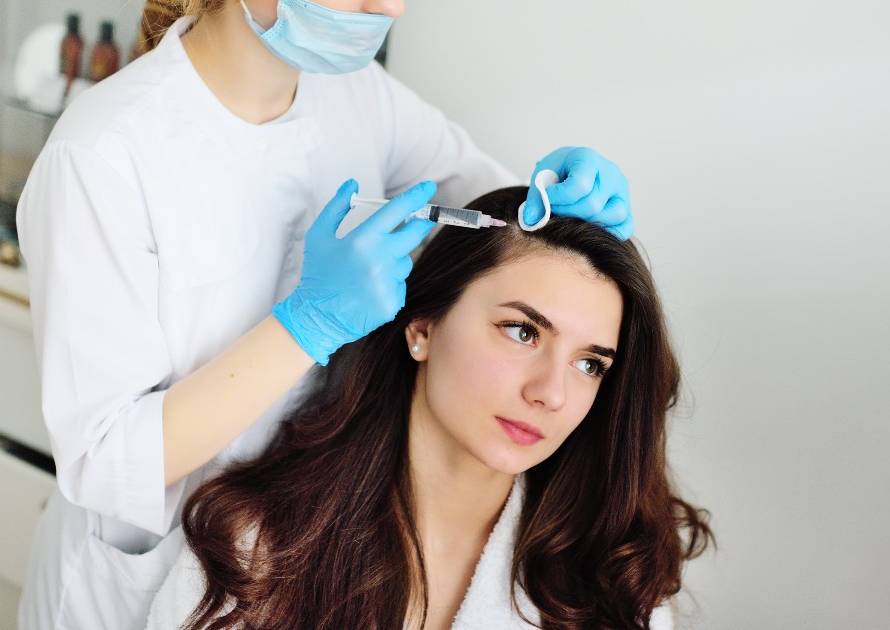
The skin is the largest organ in the body, and more often than not, it gets affected by many diseases. However, not all skin diseases have typical presentations. Sometimes, some skin diseases can be a little hard to determine and spot using typical laboratory investigations. This is why it is essential to resort to other medical diagnosis methods like biopsy.
This article will focus on the skin biopsy procedure, how it is done, aftercare tips, what to expect during the procedure, and why you might need to undergo it. Read further to know all about skin biopsy.
Overview
The skin contains multiple cell types, including Keratinocytes (skin cells), Melanocytes (pigment cells), Langerhans cells (first-line defense in the skin), and Merkel cells (sensory cells). Each type of skin cell has an essential function in the health of your skin. Moreover, the skin also has multiple layers, including Epidermis (superficial layer), Dermis (deep layer), and Subcutaneous (deepest layer).
Diagnosing skin diseases is a process that involves taking a medical history doing a physical examination for the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. If needed, the doctor will resort to doing a biopsy. After that, the doctor will do a clinicopathologic correlation to reach the final diagnosis so that they can set the treatment plan afterward.
A skin biopsy is a procedure that removes a small sample of cells or skin from your body for testing. The skin sample is examined under a microscope to check for any skin disorders, such as skin cancer, skin infections, or skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis (eczema).
The difference between regular lab tests and skin biopsy is that the layers and cells of your skin sample are looked at under the microscope during skin biopsy. The doctor would look for any presence of foreign bodies or infections. Moreover, the presence or absence of specific cells in certain patterns confirms the final diagnosis.
Note: If your doctor recommended that you undergo a skin biopsy, do not use any medication or apply creams before the procedure because that might mask skin changes which would ruin the skin biopsy accuracy.
Types of Skin Biopsy
There are three main types of skin biopsies, these are:
- Shave biopsy: The doctor uses a tool similar to a razor to remove a small section of the top layers of skin (epidermis and a portion of the dermis).
- Punch biopsy: The doctor uses a circular tool to remove a small core of skin, including deeper layers (epidermis, dermis, and superficial fat).
- Excisional biopsy: The doctor uses a scalpel to remove an entire lump or an area of abnormal skin, including a portion of normal skin down to or through the fatty layer of skin.
How the Skin Biopsy Procedure Goes
Skin biopsy is not an overly-complicated procedure. It is fast and simple and will not take much of your time. Here is what to expect when you undergo a skin biopsy:
- First, the doctor will select the site for the biopsy. Sometimes, multiple skin samples are taken.
- Then, the doctor will clean the selected site for the biopsy.
- After that, the doctor will apply local anesthesia.
- The doctor then takes a sample of your skin by using sterile surgical equipment. Depending on the type of autopsy, the doctor will sometimes use a blade or the punch biopsy device.
- Then, the sample is immediately added to a sterile container that contains a medium like formalin.
- After that, the doctor will seal the wound with surgical sutures.
- A healing cream and an antibiotic are then applied to the wound.
- The wound is then covered with a proper dressing.
The skin sample gets sent to the pathology lab so that the tissue gets processed. Then, it will be analyzed by a damato-pathology specialist. The results will then be discussed with Dr. Maha.
After Procedure Care
After the procedure, the doctor might instruct you to keep the bandage over the biopsy site until the next day. It is unlikely that your wound would bleed after leaving the doctor’s office. However, it can occasionally happen, most likely for people who take blood-thinning medications. If this happens to you, just apply pressure to the wound for approximately 20 minutes. If the bleeding continues after applying pressure for 40 minutes, contact your doctor immediately.
Things to do yourself after the biopsy:
- It is essential that you keep the biopsy site clean.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment to the wound site twice a day until the suture is removed.
- Suture removal depends on the location of the biopsy (face 5-7 days, trunk 7-10 days, extremities 10-14 days).
- You will need to visit the doctor’s office to have the doctor or the nurse remove your sutures.
All biopsies cause a small scar; some people develop a prominent, raised scar (keloid). A scar is more likely to form when the biopsy is done on the neck or upper torso, such as the back or chest. However, scars fade gradually, and the permanent color of the scar will be clear two years after the biopsy.
Try to avoid bumping the area or doing activities that might stretch the skin so you can prevent enlarging the scar or having the wound bleed. Do not soak in a bathtub, swimming pool, or hot tub until your doctor says it is okay to do so. Usually, you can go back to your normal daily activities about seven days after the procedure.
The wound might need several weeks to heal fully. However, the healing process is usually completed within two months of the procedure. It is important to note that wounds on the legs and feet tend to heal slower than those on other areas of the body.
Risks and Side Effects of Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy is a generally safe procedure, and although the chances are low, complications can always occur, including:
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- Scarring
- Infection
- Allergic reaction to a topical antibiotic
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Regarding Skin Biopsy
The following questions are some of the most frequently and commonly asked questions about the skin biopsy procedure.
Why Am I Being Asked to Get a Biopsy?
If your doctor has asked you to get a biopsy done, there is most probably an abnormality that is not conclusive via other lab tests. Your doctor would be recommending the biopsy to get the most accurate diagnosis of your condition.
Are Biopsies Accurate?
Yes, compared to most other testing options, a biopsy is the most accurate. It can confirm many skin diseases diagnoses, including skin cancer. Skin biopsy has also been able to identify the type of cell tumor and even tell if the tumor has a certain type of genetic modification.
What Are the Different Types of Biopsy?
There are several types of biopsies. However, the three main skin biopsy types include: shave biopsy, punch biopsy, excisional biopsy. Each one of them is done on a different layer of skin.
How Can I Prepare for a Biopsy?
Your dermatologist will give you specific guidelines about what to do before the procedure, including what to do regarding ongoing medications, supplements, and your diet. However, make sure that you do not apply any unnecessary creams, deodorants, lotions, or talcum powder on your body before the procedure.
How Soon Can I Get My Biopsy Results?
You can get your results within ten days, but it all depends on your case, analysis, and urgency of your condition.
Will I Be Sedated During the Biopsy?
This specifically depends on the type of biopsy. Still, most probably, your dermatologist will only apply topical anesthesia to the site of the biopsy.
What Is the Downtime for This Procedure? Can I Go to Work Soon After?
There is not really downtime for the biopsy procedure. However, you are advised not to avoid bumping the area or doing activities that might stretch the skin so you can prevent enlarging the scar or having the wound bleed. Do not soak in a bathtub, swimming pool, or hot tub until your doctor says it is okay to do so. Usually, you can go back to your normal daily activities about seven days after the procedure.
However, you can go to work two days after the procedure as it will only leave you with a slight feeling of discomfort.
Do I Need to Do Anything when I Come Back Home from the Procedure?
Your doctor will also tell you what to do after you go home. They will probably ask you to call them if you notice bleeding from your biopsy site after 24 hours of your procedure. If there’s a bandage, keep It on and keep the area clean and dry.
You can usually take a shower 24 hours after your biopsy. If any swelling or bruising happens, ask your doctor if you can apply ice packs on the site of biopsy for relief. Lastly, try to avoid strenuous exercises or lifting heavy objects until the wound is healed.